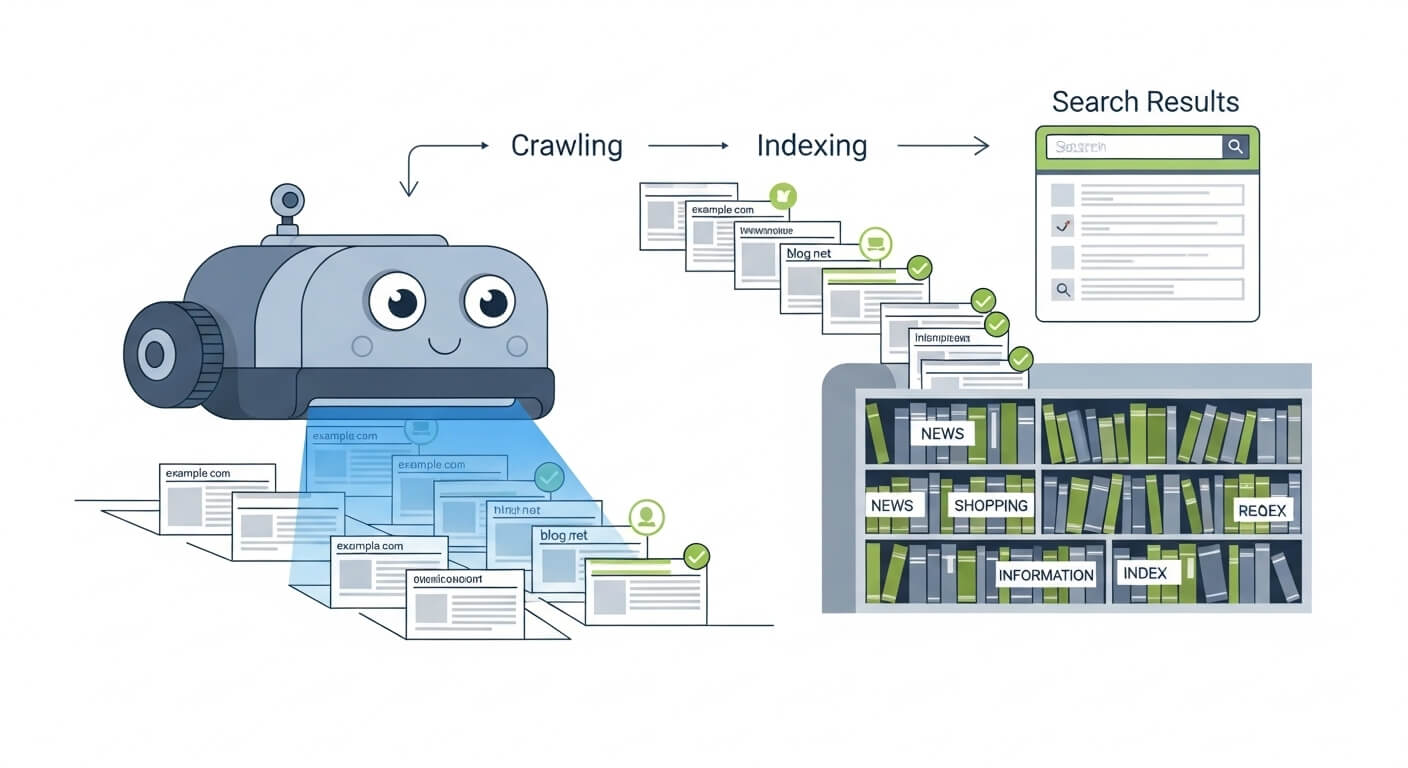
Indexing vs Crawling: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters
Introduction
If you’ve ever published a new page on your website and wondered, “Why isn’t this showing up on Google?” – you’re not alone. For many beginners in Pakistan, especially small business owners and entry-level digital marketers, the terms crawling and indexing can sound confusing or overly technical.
But here’s the good news: you don’t need to be an SEO expert to understand them.
Crawling and indexing are the two core steps Google uses to discover and store your web pages. If either step goes wrong, your page may never appear in search results; no matter how good the content is.
In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll clearly explain what crawling and indexing mean, how they work together and why understanding the difference can directly impact your website’s visibility on Google Search.
What Is Crawling?
Crawling is the discovery stage.
When you create or update a page on your website, Google doesn’t magically know it exists. Instead, Google uses automated programs called Googlebot to crawl the web.
In simple terms, crawling means:
Googlebot visits your page and reads its content.
How Google Crawls Websites
Google discovers pages in a few main ways:
- By following links from other pages (internal or external)
- Through submitted sitemaps in Google Search Console
- When a page is shared or linked elsewhere on the web
When Googlebot visits your page, it scans things like:
- Text content
- Images
- Headings
- Links
- Basic page structure
Crawling does not mean your page will appear on Google. It only means Google has seen the page.
Think of crawling like a delivery person picking up a document; it hasn’t been filed yet.
What Is Indexing?
Indexing is the storage and understanding stage.
Once Google crawls a page, it decides whether the page is good enough to be added to Google’s massive database, known as the Google index.
Indexing means:
Google stores your page and understands what it’s about, so it can appear in search results.
What Happens During Indexing
During indexing, Google tries to understand:
- What the page topic is
- Which keywords it should show for
- Whether the content is original and useful
- How the page fits compared to similar pages
Only indexed pages can rank on Google.
If your page is crawled but not indexed, it’s invisible in search results, even if it exists online.
A simple way to remember this:
- Crawling = Google visits your page
- Indexing = Google saves your page
Why the Difference Between Crawling and Indexing Matters
Many beginners assume that once Google crawls a page, it will automatically rank. That’s not true.
Here’s why the difference matters so much:
- A page can be crawled but not indexed
- A non-indexed page cannot appear in Google Search
- Rankings only apply to indexed pages
Real-World Example
You publish a blog post for your business in Islamabad. Googlebot visits the page (crawling), but Google decides:
- The content is too thin
- It’s very similar to another page
- There’s a technical issue
Result: the page is not indexed, and it never shows up in search.
This is why understanding both steps is essential for improving search visibility, especially if you’re managing your own website or learning SEO.
Common Beginner Mistakes That Prevent Indexing
One of the most common messages beginners see in Google Search Console is “Crawled – currently not indexed.” Below are beginner-friendly reasons this happens.
Thin or Low-Quality Content
Pages with very little useful information may be crawled but skipped during indexing.
Examples:
- Short service pages with only a few lines of text
- Duplicate content copied from other sites
Tip: Write content that genuinely helps users, not just search engines.
Duplicate or Very Similar Pages
If multiple pages on your site say almost the same thing, Google may index only one and ignore the rest.
Tip: Avoid creating multiple pages targeting the same keyword with nearly identical content.
Noindex Tags Added by Mistake
Sometimes a page includes a hidden instruction telling Google not to index it.
This often happens due to:
- Incorrect theme settings
- Plugin misconfigurations
Tip: Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool to check index status.
Poor Internal Linking
If a page has no links pointing to it, Google may crawl it once but not consider it important enough to index.
Tip: Link to important pages from your homepage or main navigation.
Slow or Unstable Pages
If your website loads very slowly or frequently crashes, Google may skip indexing.
Tip: Basic performance improvements can make a big difference, even for small sites.
How Crawling and Indexing Work Together
Crawling and indexing are not separate goals; they are connected steps in the same process.
- Crawling comes first
- Indexing comes second
- Rankings come after indexing
If crawling fails, indexing can’t happen.
If indexing fails, rankings are impossible.
This is why SEO isn’t just about keywords; it’s also about making your site accessible, understandable and valuable to Google.
Experienced teams like DigiCrawl often start SEO audits by checking crawl and index status before focusing on rankings, because visibility always comes first.
Conclusion
For beginners, the difference between crawling and indexing can feel small, but it has a huge impact on whether your website appears on Google or not.
To recap:
- Crawling means Google finds and reads your page
- Indexing means Google stores your page and makes it eligible to rank
- A page must be indexed before it can appear in search results
By regularly checking Google Search Console, avoiding common beginner mistakes, and focusing on helpful content, you can improve your chances of being properly indexed.
If you want to deepen your understanding of SEO and how search engines work, exploring professional digital marketing services in Islamabad or learning more about seo services in Islamabad can provide structured guidance and long-term growth.
SEO doesn’t have to be complicated – it just starts with understanding the basics.